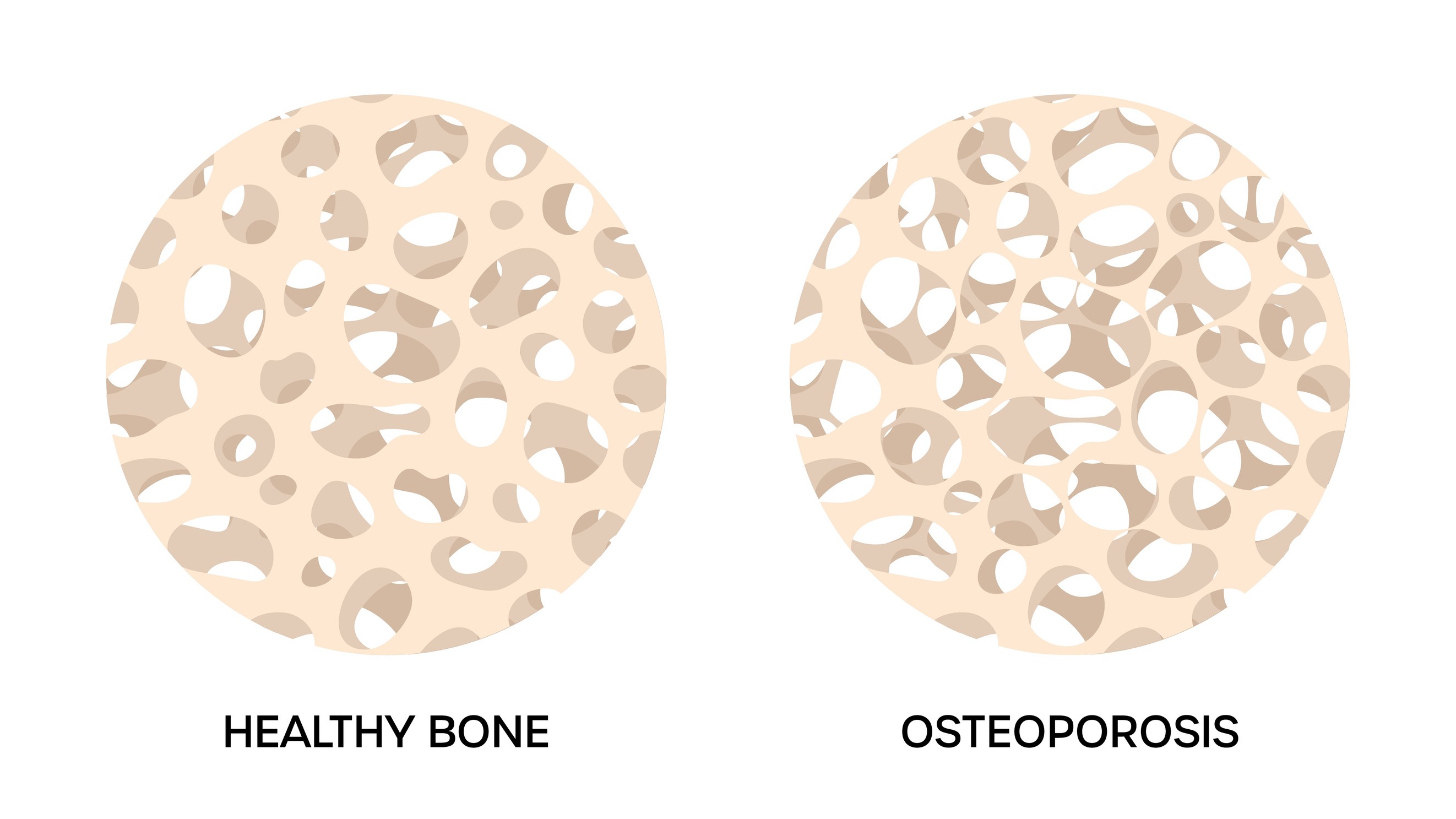
Understanding BMD's Role in Osteoporosis Treatment
The world of osteoporosis treatments is evolving, especially with the advancement in understanding bone mineral density (BMD) as a critical endpoint in clinical trials. As we look towards improved therapies, it’s essential to grasp what BMD means for patients and the medical community alike.
Why BMD Matters Now More Than Ever
The need for efficient clinical trials has become increasingly prominent, primarily due to the high costs and lengthy processes associated with traditional fracture risk assessments. The Study to Advance BMD as a Regulatory Endpoint (SABRE) has brought a fresh perspective, demonstrating that the change in %THBMD over 24 months could predict fracture risk effectively. This is a significant shift that could alleviate some of the logistical burdens on clinical research while fast-tracking the availability of new osteoporosis drugs.
Breaking Down the Study’s Findings: What Can We Expect?
The researchers utilized data from 25 clinical trials to establish an understanding of the Number Needed to Treat (NNT) based on the measured BMD changes. This insightful analysis has shown various NNT values that indicate how many patients need to be treated to prevent a fracture. Notably, the values ranged between 29 and 67 for vertebral fractures and 73 to 152 for all clinical fractures.
Transformative Implications for Future Treatments
By establishing a clear relationship between BMD changes and clinical outcomes, the SABRE study aims to aid regulatory agencies like the FDA in evaluating osteoporosis therapies. If successful, this could lead to reduced costs and quicker approval times for promising treatments. Richard Eastell, a respected figure in bone metabolism, highlighted how previous trials can inform future studies, bolstering the confidence in using BMD as a regulatory endpoint.
Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions
Despite the promising findings, it is crucial to address the skepticism surrounding the reliance on BMD changes as a predictor for long-term fracture risk. Critics might argue that focusing solely on BMD might overlook other key health factors that contribute to bone health. However, the growing body of evidence suggests that when combined with other risk factors, BMD change can establish a robust predictive model for clinicians.
Next Steps: Embracing Change in Osteoporosis Management
For those affected by osteoporosis or at risk, understanding these emerging trends is vital. If we can integrate BMD more effectively into therapeutic strategies, patients can expect more tailored treatment plans, potentially leading to better health outcomes. As we collectively encourage advancements in this field, being informed plays a crucial role in navigating personal health decisions.
Change is on the horizon, and by staying updated on these developments, you empower yourself in the journey towards enhanced well-being.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment